Overview
Biodiesel are produced from living organisms or from metabolic by-products (organic or food waste products). In order to be considered a biodiesel the fuel must contain over 80 percent renewable materials. It is originally derived from the photosynthesis process and can therefore often be referred to as a solar energy source. There are many pros and cons to using biodiesels as an energy source.
Advantages
- Doesn’t require any radical changes to switch to the use of biodiesels- unlike the difficulties in switching to other renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
- Are cheaper than fossil fuels. Many governments are now offering tax incentives to buy greener cars that run on biodiesels (ethanol being one example).
- Are considered ‘carbon neutral by some people. This is because the carbon dioxide they release when burnt is equal to the amount that the plants absorbed out of the atmosphere. Therefore, they don’t contribute to global warming. However, it does require some fuel to power the machinery on the farms where biodiesels are produced. Still, they are better than fossil fuels! Research suggests that they reduce carbon emissions by 50-60%.
- Reduce dependence on foreign oils. Oil fluctuates in price rapidly, so changing to biodiesels will help buffer against the change.
- Emit less particulate pollution than other fuels, especially diesel.
- Are renewable sources of energy as you can just keep producing more.
- Ethanol is very inexpensive to produce.
- Can help prevent engine knocking.
Biodiesel as Renewable Energy
Chemically speaking, biodiesel is the methyl ester of long chain fatty acids derived from vegetable oils animal fats. It can be used in compression ignition engines (diesel engines) directly, the engine needing minor or no modifications.
Raw Material for Biodiesel Production
Biodiesel can be commercially produced from various sources (Oil seeds both edible and non-edible, dead wood and leaves, agri-wastes, food processing wastes - both kitchen and industry etc. can be used, oil seeds being the most important, abundant and common raw material).
Different regions of the world do not have the benefit of possessing the same vegetable oil or animal fat in plentiful supply. Thus raw materials for biodiesel production have become geographically region-specific. Palm oil seeds in Malaysia, animal fats in Japan, soybean seeds and animal fats in the US, canola seeds in Canada and rapeseed and animal fats in Europe are examples. India has taken up Jatropha [Jatropha curcas] seeds as the major raw material. The plant may yield more than four times as much fuel per hectare as soybean, and more than ten times that of maize (corn). A hectare ofjatropha has been claimed to produce 1 ,892 litres offuel.
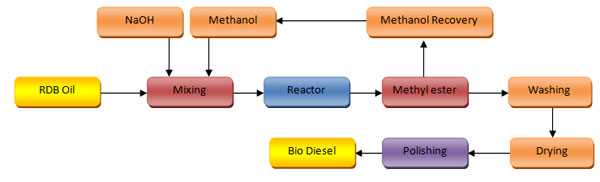
SYMFUEL Technology for Biodiesel
SYMFUEL biodiesel process uses trans-esterification reaction followed by neutralization and washing steps. The two-step trans-esterification converts nearly 100 percent of the triglycerides in the oil or fat to bio diesel (methyl ester). The excess methanol is recovered, and the biodiesel dried in the same step. Finally, the bio diesel is filtered to remove potential impurities formed below the process temperature. In essence, the steps are, trans-esterification, washing, drying and polishing.